Biology : What is The Cellulose
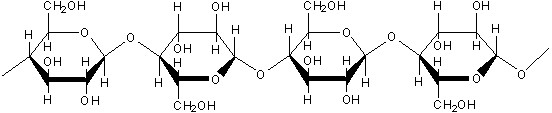
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C 6 H 10 O 5) n. He is the main content in the fiber plant, which serves as a structural component of plants. He is the main content in the fiber plant, which serves as a structural component of plants.
Cellulose is a polymer that contain adequate glucose units β anomer type that allows the cellulose to form one very long chain. Cellulose is a polymer that contain adequate glucose units β anomer type that allows the cellulose to form one very long chain.
Cellulose is insoluble in water, but soluble in a solution of hydroxide kuprik berammonia (Schweitzer test material). Cellulose is also soluble in hydrochloric berasid laruta zinc chloride. Cellulose does not give a blue color with iodine. Cellulose is insoluble in water, but soluble in a solution of hydroxide kuprik berammonia (Schweitzer test material). Cellulose is also soluble in hydrochloric acid laruta zinc chloride. Cellulose does not give a blue color with iodine.
1. Know Glycogen
Glycogen (or starch muscle)) is a type of polysaccharide whose main function is as a store of reserve energy for animal cells. Glycogen is a polymer with monomer constituent is glucose. The function of this compound is analogous to starch. Structurally, glycogen is similar to one constituent of starch, amylopectin, but more dense branches. If the amylopectin branching occurs every 24 to 30 units of glucose, the glycogen branching occurs every 8 to 12 units.
Glycogen is found in the form of granules in the cytosol in some tissues, especially in muscles and plays an important role in glucose cycle. In addition to the muscles, glycogen can be found in many other cells, such as liver, brain, and blood. Glycogen provides energy reserves that can be quickly available to meet immediate needs glucose, although not as much as can dsediakan by other energy reserves, fat (triglycerides). Only the glycogen stored in liver cells available to other organs.
Glycogen is stored carbohydrate in the form of glucose in the body that serves as a source of energy. Formed from glucose mokekul mutually bind and form more complex molecules, glycogen deposits choose a function not only as a source of energy for muscle work but also a source of energy for the central nervous system and brain.
In the body, muscle tissue and liver are the two main compartments that are used by the body to store glycogen. In muscle tissue, glycogen would contribute about 1% of the total muscle mass while in liver glycogen would contribute about 8-10% of the total mass of the liver. Despite having a smaller percentage but in total muscle tissue has a number of glycogen 2 times larger compared with the liver glycogen.
In muscle tissue, glucose is stored in the form of glycogen can be used directly by muscles for energy. So also with the heart that can be issued if required glucose to produce energy in the body. Besides the liver glycogen also have an important role in maintaining a healthy body that serves to maintain blood glucose levels.
Glycolysis is a series of biochemical reactions in which glucose is oxidized to two molecules of pyruvic acid. Glycolysis is one of the most universal metabolic processes known to us, and occurs (with variations) in many cell types in almost all forms of organisms. The process of glycolysis alone produces less energy per molecule of glucose compared with the perfect aerobic oxidation.
Related Post :
cellulose, the notion of cellulose, cellulose picture, glycogen
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C 6 H 10 O 5) n. He is the main content in the fiber plant, which serves as a structural component of plants. He is the main content in the fiber plant, which serves as a structural component of plants.
Cellulose is a polymer that contain adequate glucose units β anomer type that allows the cellulose to form one very long chain. Cellulose is a polymer that contain adequate glucose units β anomer type that allows the cellulose to form one very long chain.
Cellulose is insoluble in water, but soluble in a solution of hydroxide kuprik berammonia (Schweitzer test material). Cellulose is also soluble in hydrochloric berasid laruta zinc chloride. Cellulose does not give a blue color with iodine. Cellulose is insoluble in water, but soluble in a solution of hydroxide kuprik berammonia (Schweitzer test material). Cellulose is also soluble in hydrochloric acid laruta zinc chloride. Cellulose does not give a blue color with iodine.

1. Know Glycogen
Glycogen (or starch muscle)) is a type of polysaccharide whose main function is as a store of reserve energy for animal cells. Glycogen is a polymer with monomer constituent is glucose. The function of this compound is analogous to starch. Structurally, glycogen is similar to one constituent of starch, amylopectin, but more dense branches. If the amylopectin branching occurs every 24 to 30 units of glucose, the glycogen branching occurs every 8 to 12 units.
Glycogen is found in the form of granules in the cytosol in some tissues, especially in muscles and plays an important role in glucose cycle. In addition to the muscles, glycogen can be found in many other cells, such as liver, brain, and blood. Glycogen provides energy reserves that can be quickly available to meet immediate needs glucose, although not as much as can dsediakan by other energy reserves, fat (triglycerides). Only the glycogen stored in liver cells available to other organs.
Glycogen is stored carbohydrate in the form of glucose in the body that serves as a source of energy. Formed from glucose mokekul mutually bind and form more complex molecules, glycogen deposits choose a function not only as a source of energy for muscle work but also a source of energy for the central nervous system and brain.
In the body, muscle tissue and liver are the two main compartments that are used by the body to store glycogen. In muscle tissue, glycogen would contribute about 1% of the total muscle mass while in liver glycogen would contribute about 8-10% of the total mass of the liver. Despite having a smaller percentage but in total muscle tissue has a number of glycogen 2 times larger compared with the liver glycogen.
In muscle tissue, glucose is stored in the form of glycogen can be used directly by muscles for energy. So also with the heart that can be issued if required glucose to produce energy in the body. Besides the liver glycogen also have an important role in maintaining a healthy body that serves to maintain blood glucose levels.
Glycolysis is a series of biochemical reactions in which glucose is oxidized to two molecules of pyruvic acid. Glycolysis is one of the most universal metabolic processes known to us, and occurs (with variations) in many cell types in almost all forms of organisms. The process of glycolysis alone produces less energy per molecule of glucose compared with the perfect aerobic oxidation.
Related Post :
cellulose, the notion of cellulose, cellulose picture, glycogen
0 comments:
Posting Komentar